Fracture Types: Tibia And Fibula Bone Models Visually Aid In Reduction And Fixation
The success of reduction and fixation procedures on tibia and fibula fractures depends on correct alignment and reconnection. Tibia and fibula bone model sets can help orthopaedic surgeons perfect their technique to minimize error and ensure the maximal chance of success in treating different lower extremity fractures.
Tibia Fracture Types
Tibial fractures are the third most common long bone fracture among children and represent about 15% of all pediatric fractures. Their common occurrence demands mastery of surgical reduction and fixation techniques among orthopaedic surgeons. A high quality tibia and fibula bone model can help medical students practice various fracture treatments like the ones below:
|
Fracture Types |
Bone Model Training |
|
Proximal Tibial Fractures Ex. Proximal tibial epiphyseal fracture Proximal tibial metaphyseal fracture |
|
|
Tibial Shaft Fractures
|
• insertion of guidewire and pins • drilling • nail insertion • placement of screws
|
|
Distal Tibial Fractures |
|
Fibula Fracture Types
Though the fibula does not carry as much weight as the tibia, it is prone to fractures due to stress and direct impact. A tibia and fibula bone model give orthopaedic trainees a firm grasp of anatomical details relevant to fibula fractures. Here are some examples of how bone models act as a visual aid in practicing treatment techniques for fibula fractures:
|
Fracture Types |
Bone Model Training |
|
Fibular head fracture |
Proper reduction techniques of fibular head fracture and displacement can be practiced repetitively to ensure against knee instability and early arthrosis. |
|
Lateral malleolus fracture |
Proper insertion of screws can be emphasized to avoid the application of too much pressure on the thin fibula, such as those used to treat lateral malleolus fractures. |
|
Avulsion fracture |
Bone models provide invaluable visualization aid to conservative reduction techniques often prescribed for fibular avulsion fracture, especially for minor displacements. |
|
Stress fracture |
Proper management of fibular stress fractures through conservative reduction treatment can be emphasized as it helps avoid unnecessary surgical fixation. |
|
Shaft fracture |
• Proper manipulation of reduction tools such as lobster and pointed clamps can be practiced on bone models depicting displaced, comminuted fractures of the fibular shaft. • Fibular fixation techniques including plate placement and screw insertion can be applied to bone models. |
Tibia and Fibula Bone Model Options
The different tibia and fibula bone model options are available for training programs. Foam-based models are best for training fixation techniques as they are easier to drill. They are also conducive to practicing screw insertion and plate fixation. Some models are equipped with inner cancellous material to mimic real bone.
|
Foam Cortical Shell Tibia with Bicondylar and Transverse Fractures |
Solid Foam Tibia and Fibula, Solid Foam, Medium
|
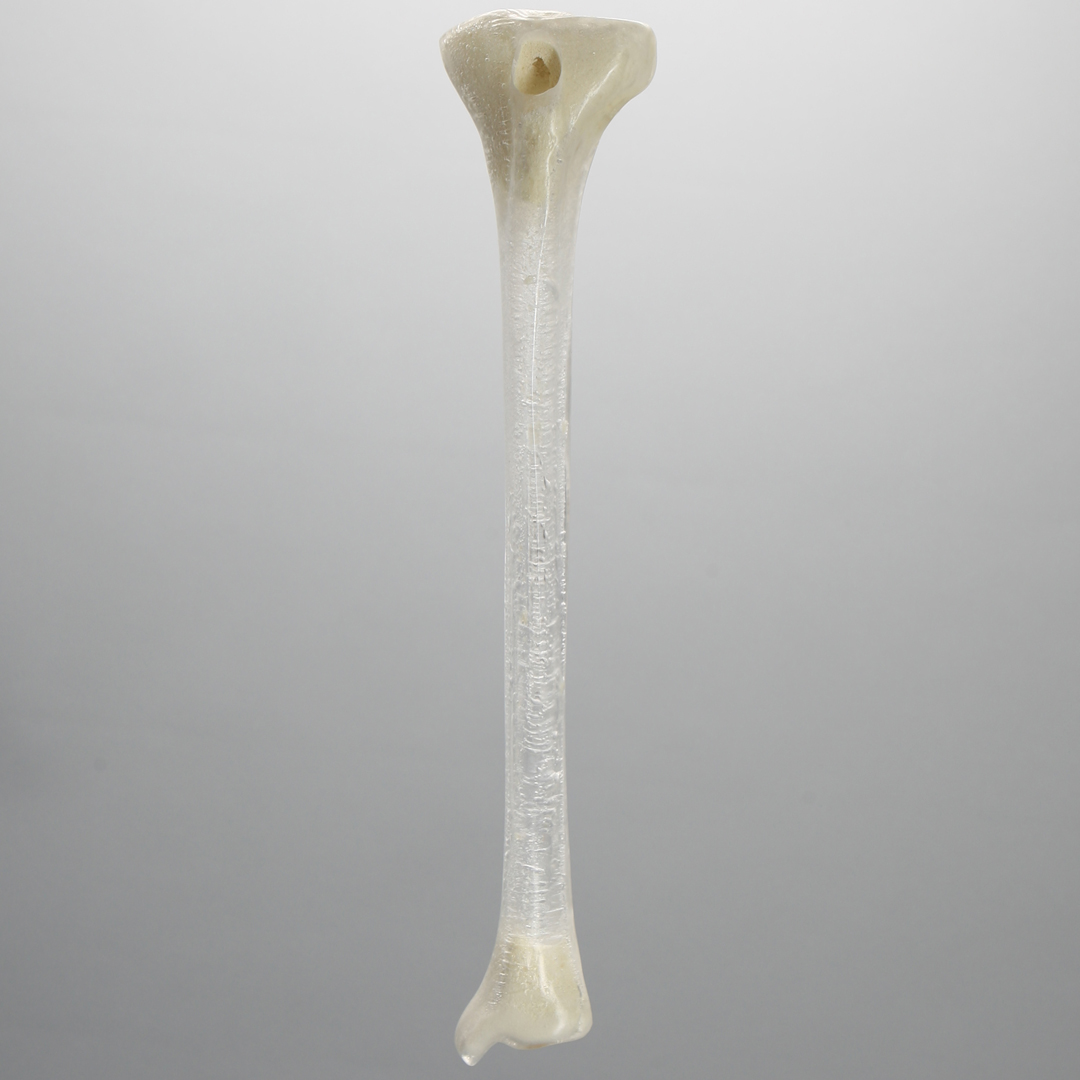
Plastic-based bone models are great for training reduction techniques as they are very durable. Plastic models are designed for repeated use and handling.
|
Plastic Cortical Shell
|
Transparent Cortical Shell Tibia with 13 mm Entry Site for IM Nail, Left
|
In summary, tibia, and fibula bone model sets aid visualization in procedure training, especially in closed reduction techniques. Bone models enable surgical trainees and orthopaedic students to practice fixation techniques like drilling, screw insertion, and plate fixation. Foam-based bone models are best for fixation practice while durable plastic models are better used for repetitive practice of reduction techniques.
Best-in-Class Models For Hands-On Orthopaedic Training
Sawbones offers best-in-class tibia and fibula bone model sets for orthopaedic training and medical education. Sawbones is known for originating hands-on workshop models and continues its leadership today in the manufacturing of anatomical medical training models. We offer different options including foam, plastic, and radiopaque models. For more information on our offerings or to talk about custom training models, contact us at 206-463-5551.

If you're seeking something you can't find on our website, our sales team is happy to help. We can either direct you to the right model or provide a free quote on the right custom project to meet your needs. Discover options with our clear bone models, laminated blocks, custom displays, or other machining projects.