Using Surgical Demonstration Models Will Change the Way You Teach (and How They Learn)
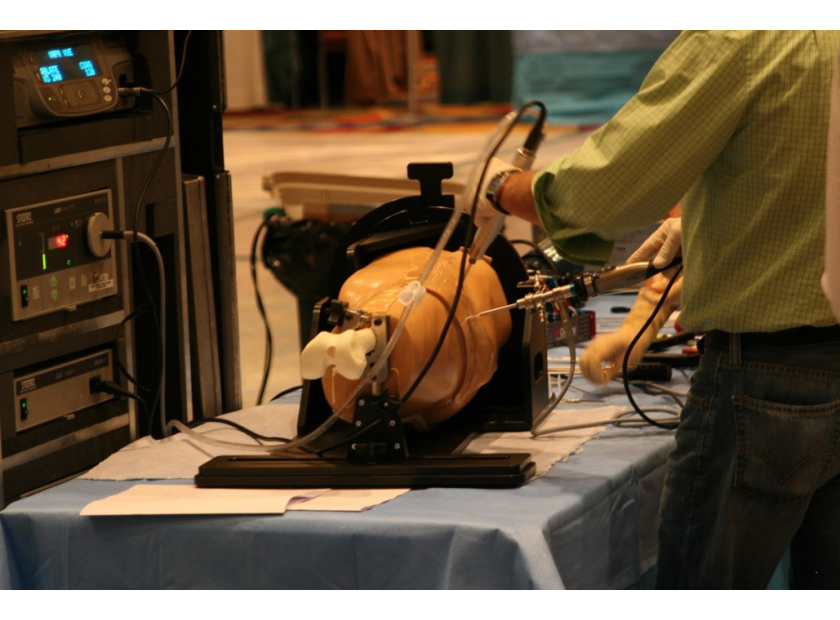
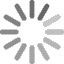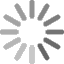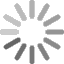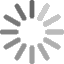
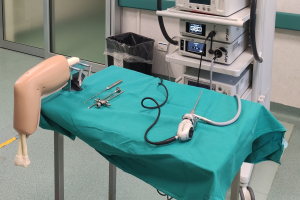
Surgical demonstration models are changing medical education by making it more accessible. In the past, student training options were limited. Their practical experience depended on unsophisticated models or hard-to-obtain cadavers. Today's surgical demonstration models are far more realistic, leading to more in-depth education.
Of course, it may be challenging to choose the right ones with so many options out there. While medical teachers may want to go to the more advanced, all-inclusive training models, that's not always necessary. This is especially true when the same model will require repeated use to complete demonstrations.
Focusing Models for Surgical Demonstrations
Surgical demonstrations will come early in the training process, typically before students are ready for hands-on experience. Consequently, the medical training model needs to be solely focused on a single procedure, or at the very least, operations in the same area. Some common choices include:
- Fracture reduction and casting: Closed reduction of fractures is challenging to learn, but the right models help students understand what to look for when setting a bone, regardless of the complexity of the damage. The ability to see this and different casting strategies in action goes a long way towards building confidence.
- Reconstruction: Reconstructive surgery is incredibly complex, whether the surgeon wants to restore function or make cosmetic changes. These procedures are continually being refined, so continuing education models are necessary to teach the use of new techniques, tools, or materials.
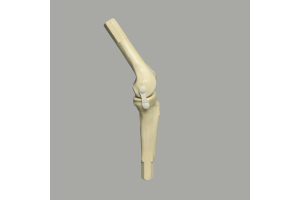
- Arthroscopy: Keyhole surgery, minimally invasive surgery (MIS), laparoscopic surgery, and bandaid surgery all require precision and attention to detail. A trainee may have to see multiple arthroscopies before they're ready to practice on their own model, and especially before moving onto a cadaver. These models can be incredibly complex.
- Injections: Injection training requires everything from a simple practice vaccine to arthrocentesis in the aspiration of fluids. This process demands advanced realism to ensure a thorough understanding and greater precision.
- Grafts: Graft training may include the harvesting of materials for the graft or the applications of those materials themselves. These are both highly delicate procedures where even the smallest error could damage an expensive model irrevocably.
On top of these popular surgical demonstration models, instructions may want more general options to demonstrate suture types or show ways to diagnose a specific injury or disease. Before choosing, it's essential to understand the particular features available, so they know which one will best suit their needs.
Ideal Features on Surgical Demonstration Models
Physical models have many advantages in surgical training over simple text or lectures. They allow the student to see a procedure in action. Some premium model features will enhance the learning process even more. Consider if the following features could deepen your students’ learning:
Dual purpose |
Reusable |
Haptic feedback |
Realism |
Buildable |
|
Every surgery with an arthroscopic option also has an open counterpart. Surgical models that allow instructors to show both are invaluable, as they work for multiple lessons. While this isn't always available or even necessary, it's still a great option. |
As this is demonstration only, instructors don't want to destroy the model when showing a procedure. Replaceable skins, reusable portals, and other features allow instructors to provide the lesson without the need to discard or damage the whole part. |
Haptic feedback is essential when working in closed systems, as there need to be some indicators of success or failure. This option provides an alert when an internal structure comes in contact with an instrument, so it's ideal for injection or arthrocentesis lessons. |
Some procedures require a bit more in-depth realism to show students what to expect. A good example lies in arthrocentesis, where a needle pulls fluid from a joint. The ability to remove fluid that's the right color and consistency is vital for effective teaching. |
Ideally, trainers can teach students one procedure and then add on features to increase complexity. For example, the ability to teach both an ACL and meniscal repair on the same model is ideal, as the surgeries often occur simultaneously or in close proximity to each other. |
Selecting the Most Effective Surgical Demonstration Model
The use of surgical demonstration models can take teaching to the next level, but only if they provide the realism and feedback needed to recreate the surgical experience. While demonstration models don't have to be as detailed as working models, a higher level of sophistication ensures a better training experience. Features like buildability, haptic feedback, reusability, and multipurpose options are ideal add-ons. In the right environment, these models can replace hard-to-obtain cadavers or less effective simulations to allow for in-depth learning.
Sawbones provides surgical demonstration models for a wide range of procedures and specialties. Review our catalog to see our offerings, or contact us at 206-463-5551 to discover our solutions.

If you're seeking something you can't find on our website, our sales team is happy to help. We can either direct you to the right model or provide a free quote on the right custom project to meet your needs. Discover options with our clear bone models, laminated blocks, custom displays, or other machining projects.